This definition of sustainable forestry has been adopted by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations and Forest Europe (the pan-European forest collaboration, of which Sweden is a part):
"The stewardship and use of forests and forest lands in a way, and at a rate, that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, regeneration capacity, vitality and their potential to fulfill, now and in the future, relevant ecological, economic and social functions, at local, national, and global levels, and that does not cause damage to other ecosystems."
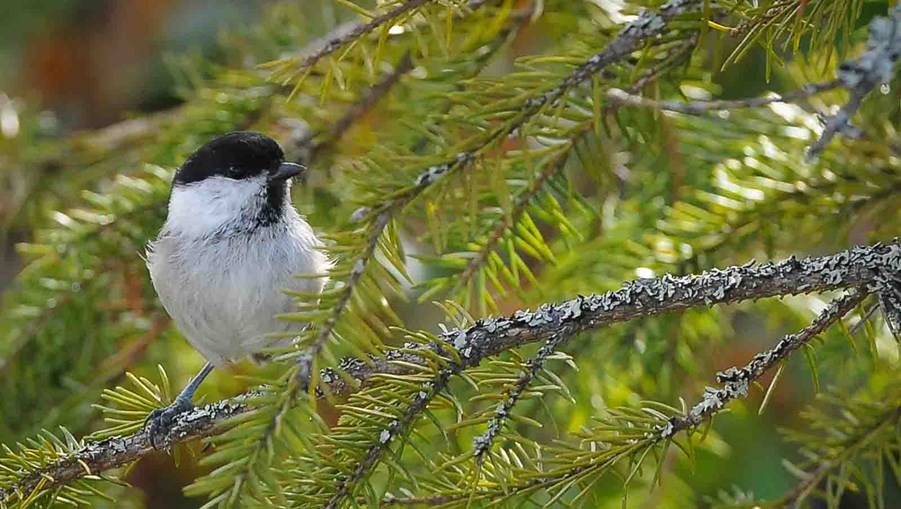
Ecological sustainability
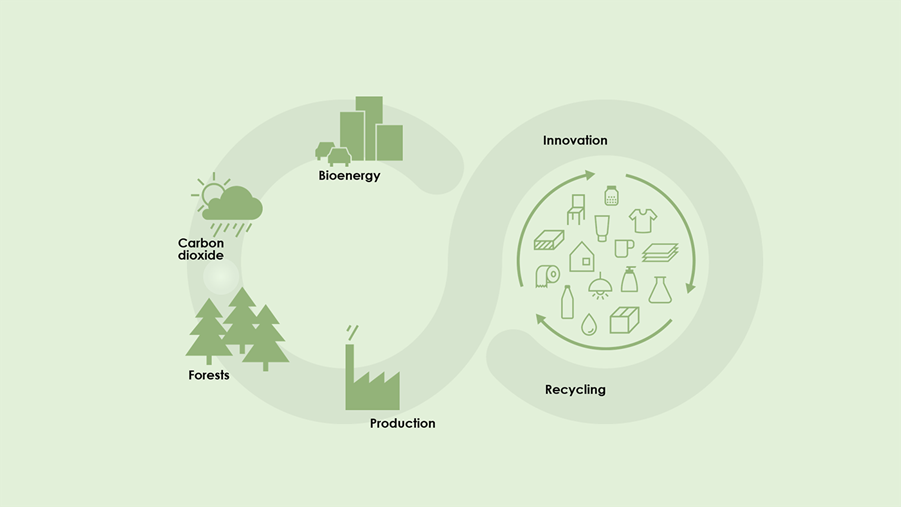
Sustainable forestry secures the long-term availability of renewable resources, protects biodiversity and helps to combat global warming. The Swedish forest sector’s goal is to manage the forest to ensure that all species in Sweden’s wooded landscape can survive and thrive. By taking care in managing the forest, the conditions that promote biodiversity are created every day.
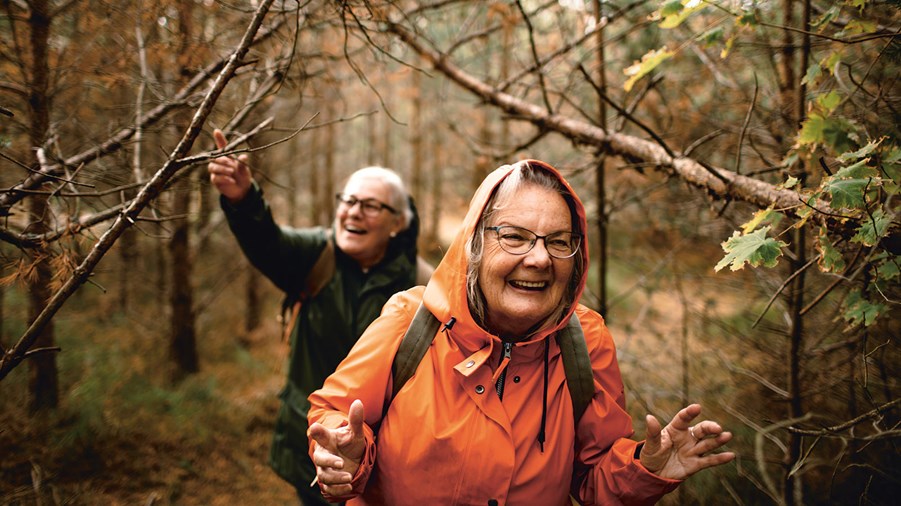
Social sustainability
The forest sector bears a social responsibility both as an employer and as a player in society. The sector enables people to live and work in all parts of Sweden, and in many areas it is a vital hub in the local community. Other aspects of social sustainability relate for example to the sector’s efforts to make the forest an important place for recreation and being outdoors.
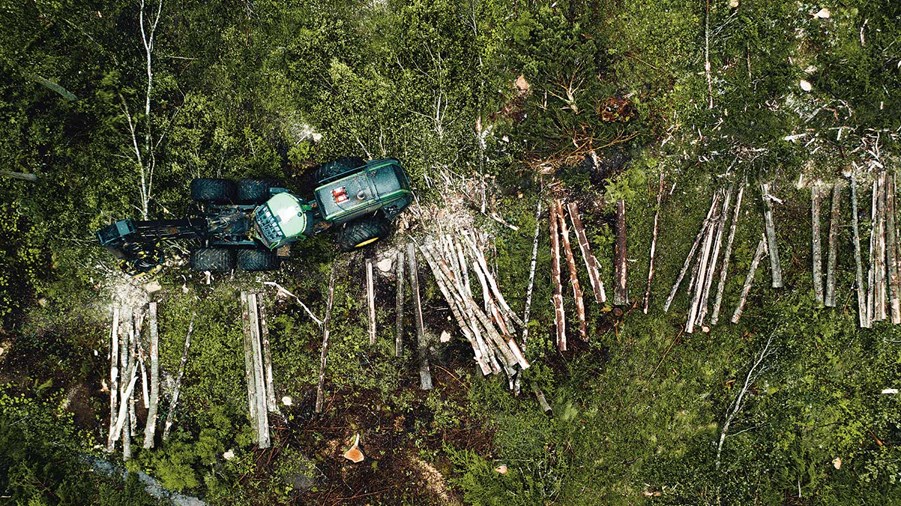
Economic sustainability
The forest should be used in a responsible, profitable way, always creating competitiveness and increased value for coming generations. With the vision “The forest sector drives growth in the global bioeconomy”, the sector wants to work for sustainable economic growth based on renewable biobased materials.
Sustainable forestry
The sustainable Swedish model of forestry is based on three pillars: ecological, economical and social sustainability.